Introduction
In a world that is rapidly digitalizing, the need for a secure, transparent, and decentralized mode of operations is ever-increasing. Enter the realm of Blockchain, a groundbreaking technology that has revolutionized industries across the globe. But how does it connect to mobile applications? Let's delve deeper.
Blockchain, at its core, is a distributed ledger that maintains a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are secured using cryptography. The most compelling feature of Blockchain is its invulnerability to data modification, instilling the technology with trust, transparency, and security.
Riding on the backbone of Blockchain, we come across the popular Web3. Web3 or Web 3.0, represents the new era of the internet - one that is built on the principles of decentralization. Web3 aims to create an online environment where users maintain control over their own data and interactions, a concept that is inherently symbiotic with Blockchain.
Based on that, we can tell that the integration of Blockchain and Web3 into mobile apps holds tremendous potential and is set to revolutionize various industries. Some key areas where we can expect to see the impact could be: decentralized finance, in-app digital identity or decentralized social networks, among others.
Therefore, we realized the potential of using this technology in mobile apps and decided to catch up within our team. Basically, we decided to create an initial, simple project where we could establish an environment for experimentation and gain practical experience with Blockchain. Furthermore, we aimed to leverage this experience for future projects.
In the following sections, we will introduce you to some crucial terminologies associated with Blockchain and share the idea behind our city hall app leveraging Blockchain. In the future, we will publish a second post to discuss its development process and technological background.
This journey will provide you insights into the future of Blockchain technology within the realm of mobile apps, and how it's set to revolutionize the way we engage with digital platforms. So, get ready for an intriguing exploration into the world of Blockchain and mobile applications. Let's delve in!
Some new terminologies
dApps
dApps stands for Decentralized Applications. dApps are software applications that run on a decentralized network, typically utilizing blockchain technology. Unlike traditional applications that rely on centralized servers, dApps operate on a network where data and transactions are distributed across multiple nodes. A node is a computer or device that maintains a copy of the entire blockchain and verifies the validity of transactions.
Key features:
-
Decentralization: dApps operate on a decentralized network, which means there is no single point of control or failure. The application's logic and data are stored and processed on a blockchain or similar distributed ledger technology.
-
Open Source: dApps are often open source, meaning their source code is publicly available and transparent.
-
Tokenization: Many dApps have their own native tokens or cryptocurrencies that facilitate transactions within the application or represent ownership rights and value.
-
Smart Contracts: A smart contract in dapps is an automated, self-executing program that enforces predefined rules on a blockchain.
In this article, we describe the development of a simple dApp with decentralized features and smart contracts.
Smart Contract
A smart contract is a computer program that automates, verifies, and enforces the terms of a contract or agreement between multiple parties. It is a self-executing contract with the terms and conditions directly written into code.
The key characteristics of a smart contract include:
-
Automation: A smart contract automatically executes actions or transactions when predefined conditions are met. It eliminates the need for intermediaries or centralized authorities, as the code itself enforces the terms.
-
Digital and Immutable: Smart contracts exist in a digital form, written in code, and are stored on a blockchain. Once deployed, the code becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or tampered with.
-
Decentralization: Smart contracts operate on a decentralized network, such as a blockchain, where multiple participants validate and record transactions. This decentralized nature ensures transparency and removes the need for a single central authority.
-
Trust and Security: Smart contracts leverage cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and ensure that parties involved can trust the execution and outcome of the contract. The decentralized consensus mechanism of the blockchain adds an extra layer of security.
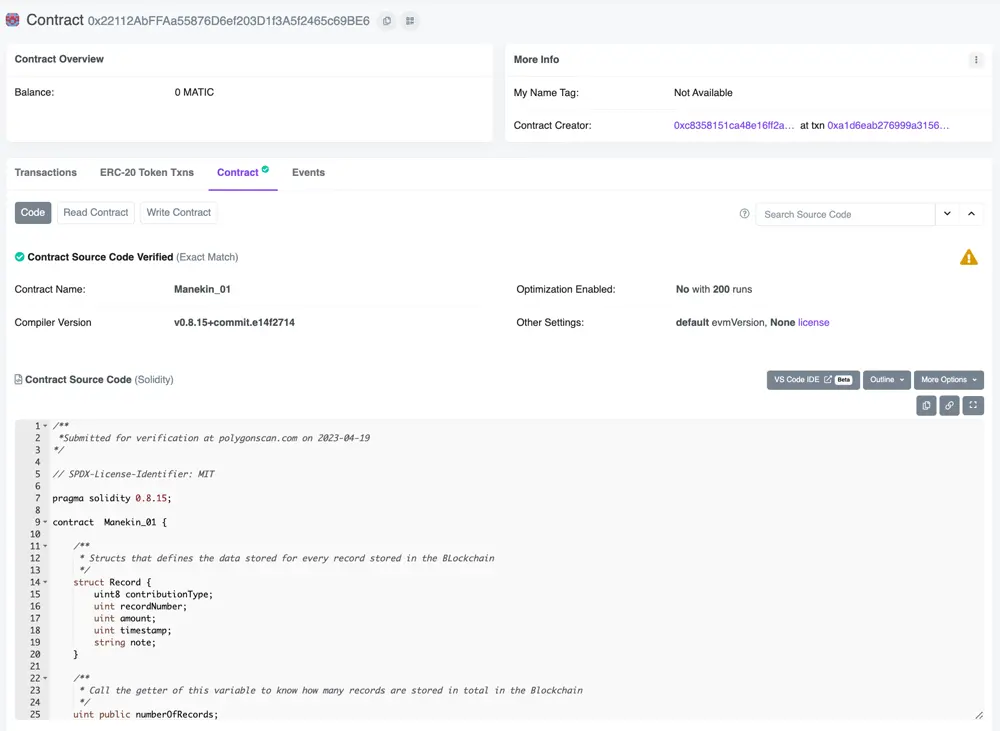
For the project described in this article, in order to deploy smart contracts and add records to the blockchain we created a wallet in Metamask.
Wallet
A Web3 wallet is a cryptographic tool that empowers individuals to exercise control over their digital identity, assets, and interactions in the decentralized landscape. It encapsulates a combination of secure key management, authentication mechanisms, and user-friendly interfaces, allowing users to securely store, send, receive, and manage their blockchain-based assets while seamlessly interacting with dApps and blockchain networks.
For the project described in this article we created a Wallet in Metamask. Metamask functions as a bridge between the user and the blockchain network by a browser extension.
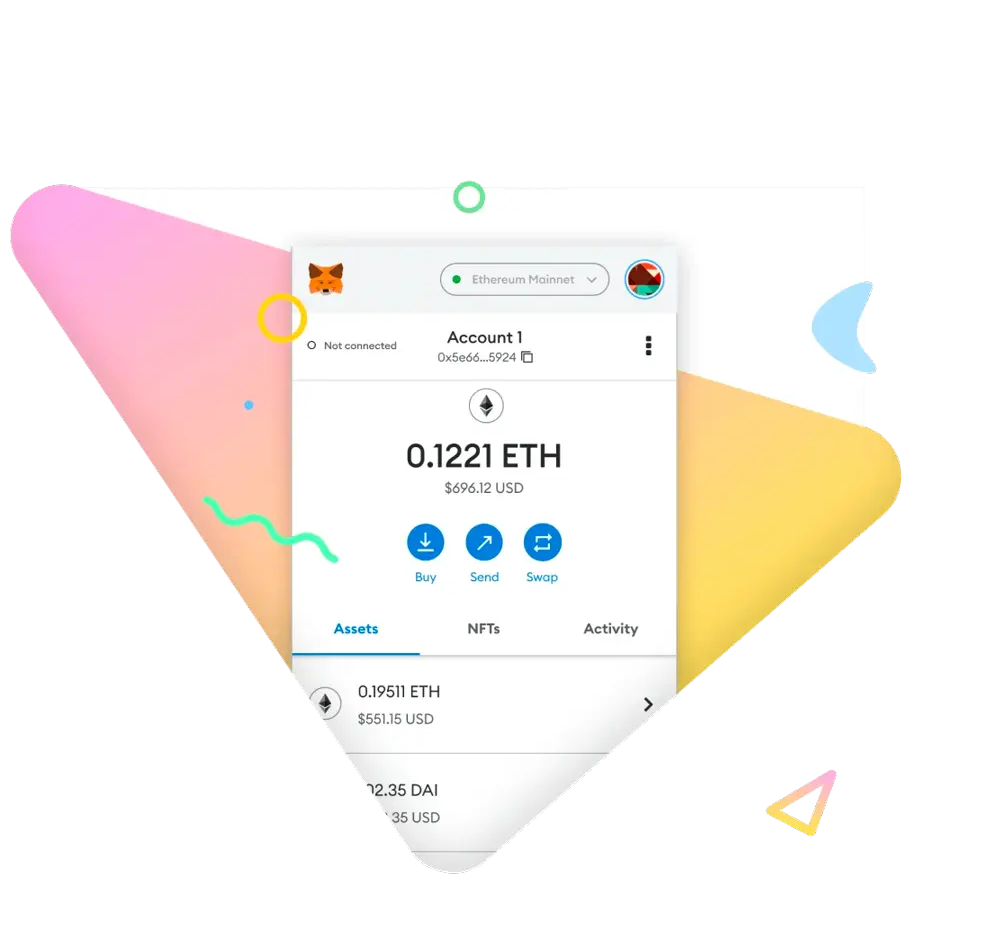
All operations that triggered a modification in the blockchain, including the creation of the smart contract, transfers of tokens, or addition of records, are recorded in transactions that are visible in the Metamask Wallet.
Transactions
A transaction is an operation executed in a blockchain. Such operations involve interacting with a smart contract, the contract's code is executed according to the specified function call and parameters. The smart contract may modify its internal state, update balances, emit events, or trigger further actions based on the transaction's logic.
When a transaction is triggered on a blockchain network, several steps occur:
-
Initiation and Validation: The transaction is created and initiated by a user or an application. Then, the transaction is broadcasted to the blockchain network, where it undergoes a validation process. Miners (in a proof-of-work network) or validators (in a proof-of-stake network) verify the transaction's validity by checking if the sender has sufficient funds, the transaction format is correct, and any additional conditions imposed by the network's consensus rules are met.
-
Inclusion in a Block: Once the transaction is validated, it is grouped together with other validated transactions to form a block. The block contains a collection of transactions and serves as a permanent record on the blockchain.
-
Mining or Block Finalization: Mining in a blockchain is the process of validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain while earning rewards for doing so. On the other hand, miners in a blockchain are participants who use computational power to verify and process transactions, adding them to the blockchain and ensuring the network's security and consensus. They are rewarded with cryptocurrency for their efforts. In a proof-of-work network, miners compete to solve a cryptographic puzzle, which requires computational effort. The first miner to solve the puzzle adds the new block (containing the transaction) to the blockchain. In a proof-of-stake network, validators take turns adding blocks based on their stake and selection algorithms.
-
Consensus and Confirmation: The newly added block is propagated to other nodes in the network, and they validate and confirm its inclusion. Confirmations represent the number of subsequent blocks added to the blockchain on top of the block containing the transaction. The more confirmations a transaction receives, the higher its finality and security.
-
Updating the Blockchain State: After the transaction is executed, the state of the blockchain is updated to reflect the changes. This includes updating account balances, modifying the state of the smart contract, and recording any relevant events or logs associated with the transaction.
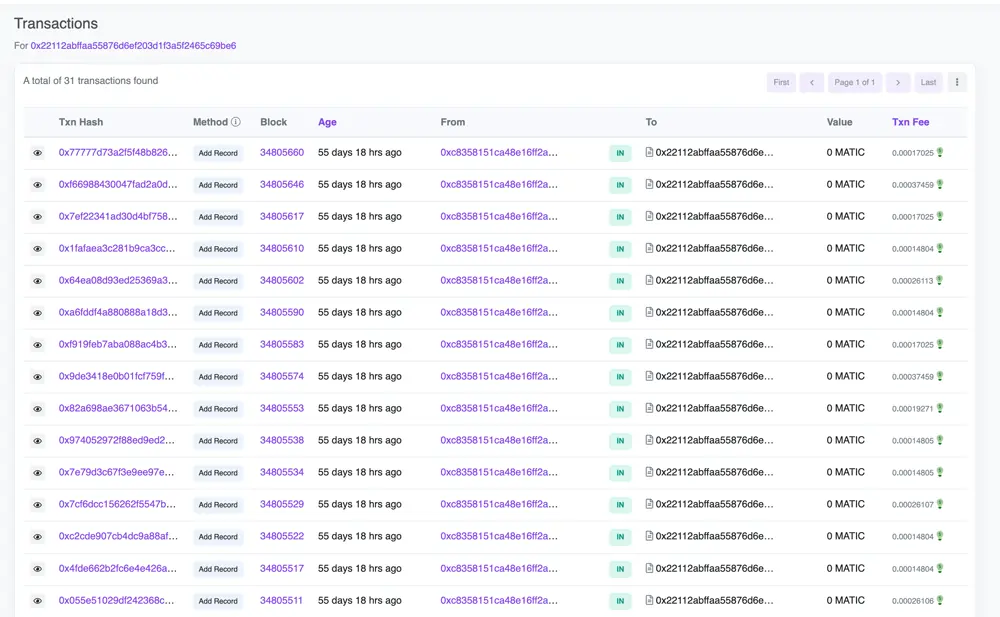
In the project described in this article, only two kinds of transactions were executed:
-
When deploying a smart contract.
-
When adding Pension and Tax records to the blockchain by invoking a method that updated the state in the blockchain.
Our Idea: A City Hall residence tax records app
The project in this blog post is a mobile application that allows users to verify their pension and tax records stored on the blockchain. For easy understanding, we called the app Manekin which stands for Money + Kin (Kin means money in Japanese, then マネー + 金 =マネキン) .
We thought that this kind of app would be a potential idea to be developed on a blockchain-based system instead of a typical cloud-based system in the upcoming years. The reason is that by storing pension and tax records on a blockchain, trust and security will be enhanced, because the data retrieved from the blockchain is immutable and reliable. However, it is important to note that blockchain technology may not be suitable for all types of applications, and in a real product, many constraints such as scalability and performance should be taken into account when designing a dApp.
These are the main features of our app:
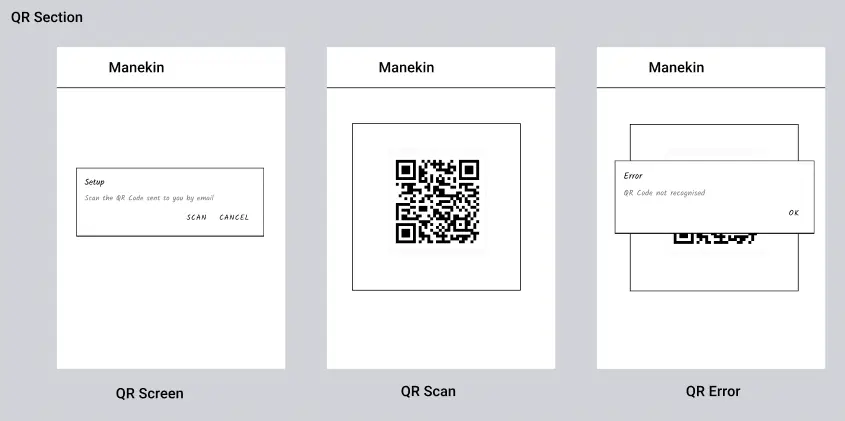
- User authentication:
- The app provides a login process where users can authenticate by entering their user id.
- The user id can be entered by scanning a QR code or manually through a text field.
- User authentication ensures that only authorized individuals can access their specific records.
- Logout process, stops access to the records until the next login.
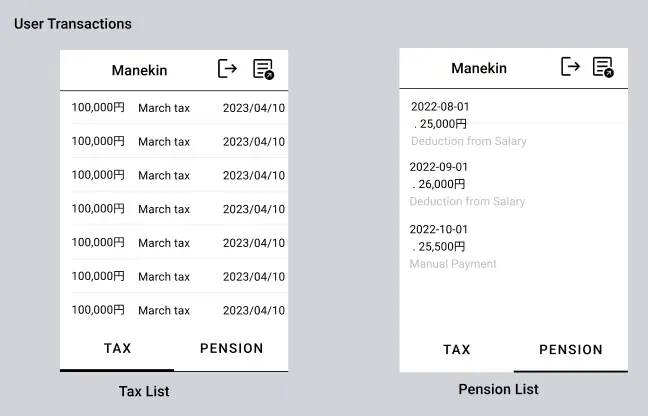
- Tax and pension records retrieval:
- The app invokes a method in the smart contract, which interacts with the blockchain and retrieves the records associated with the user id.
- The retrieved records include details such as the paid amount, timestamp, contribution type (tax or pension) and a note with relevant information about the record.
- User-friendly interface:
- We offer an intuitive and user-friendly interface with easy-to-navigate screens.
- The application communicates with a smart contract and is deployed on a Blockchain Test network. This all goes under the hood and the user has the experience as a normal database.
- By providing a user-friendly interface and seamless integration with the smart contract, the app enables users to securely access and review their records.
Beyond a City Hall app
The above idea is an idea from the digital identity and security field, where users have control over their personal data and information is more secure without relying on traditional centralized authentication systems. Digital identity and security is one of the areas expected to see an impact using Blockchain technology in the near future. Other examples from other areas could be:
-
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): A bank app enabling users to access decentralized financial services, such as lending, borrowing, and trading cryptocurrencies, directly from their smartphones. Blockchain-based smart contracts ensure transparency and security in financial transactions, allowing for peer-to-peer interactions without intermediaries.
-
Supply Chain Management: A fashion brand integrated with blockchain technology. This one could track and verify the provenance and authenticity of products throughout the supply chain. This transparency helps in combating counterfeit goods, ensuring fair trade practices, and enhancing consumer trust.
-
Decentralized Social Networking: Web3-powered mobile apps can enable decentralized social networking, where users have control over their data and interactions. They can participate in social platforms without concerns about data breaches or censorship, as content is distributed across a decentralized network.
-
Voting and Governance: An elections app could enable secure and transparent voting systems, ensuring the integrity of elections and decision-making processes. Web3 principles of decentralization and immutability enhance trust and participation in governance.
The integration of Blockchain and Web3 into mobile apps expands the possibilities for user-centric, secure, and transparent experiences. As the technology evolves and user adoption increases, we can expect to witness a paradigm shift in how we interact with mobile applications, empowering individuals and transforming various industries.
To be continued...
In conclusion, the integration of Blockchain and Web3 into mobile apps marks an exciting frontier in technology and innovation. The decentralized nature of blockchain technology, coupled with the principles of Web3, empowers individuals with greater control over their data, privacy, and digital interactions.
The potential of Blockchain and Web3 in mobile apps is vast, and as the technology advances, we can anticipate even more innovative use cases. Developers and entrepreneurs are increasingly exploring these possibilities, paving the way for a decentralized future where individuals have greater control and ownership over their digital lives.
In the next blog post, we will delve deeper into the development phase and how we did it to develop an app using this new evolving technology. Stay tuned to learn more about it.
Author

Harol Higuera
Mobile Tech Lead





